Animal & Plant Cells
Animals
- The main features of animals:
- They are?multicellular
- Their cells contain a?nucleus?with a?distinct membrane
- Their cells?do not?have?cellulose cell walls
- Their cells?do not?contain?chloroplasts?(so they?are unable?to carry out?photosynthesis)
- They feed on organic substances made by other living things
- They often store carbohydrates as?glycogen
- They usually have?nervous coordination
- They are able to?move?from place to place
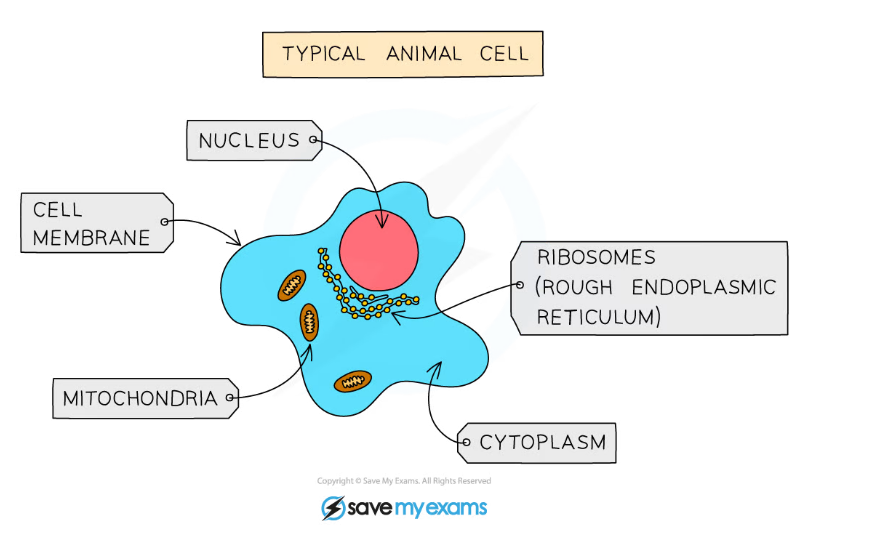 A typical animal cell
A typical animal cell
Plants
- The main features of plants:
- They are?multicellular
- Their cells contain a?nucleus?with a?distinct membrane
- Their cells have?cell walls?made out of?cellulose
- Their cells contain?chloroplasts?(so they can carry out?photosynthesis)
- They feed by?photosynthesis
- They store carbohydrates as?starch?or?sucrose
- They?do not?have nervous coordination
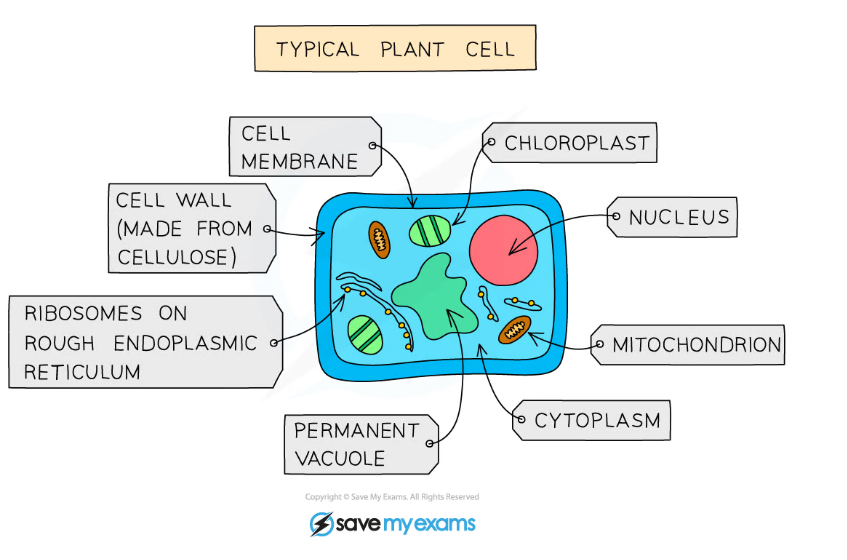
A typical plant cell
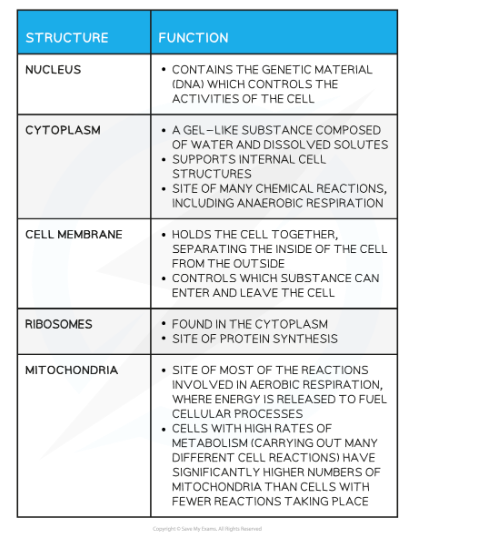
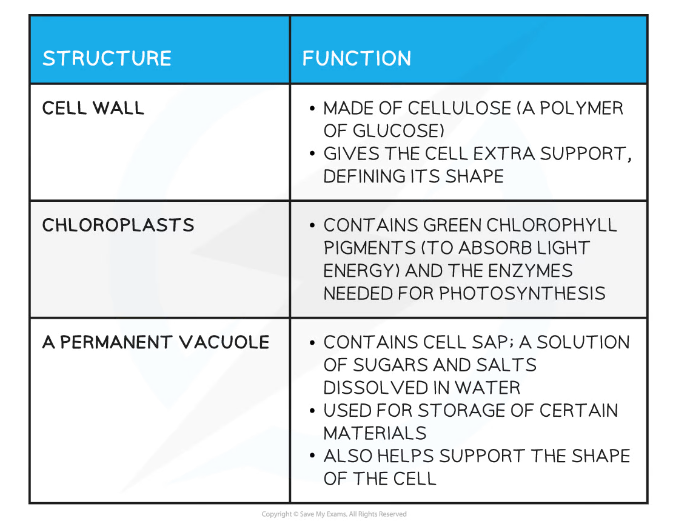
Cell Structures Found in Both Animal and Plant Cells Table
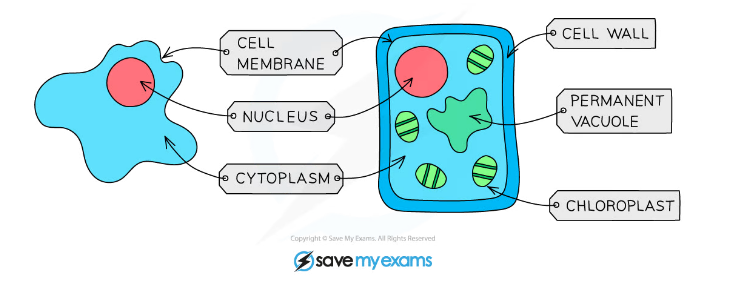
An animal and plant cell as seen under a light microscope
Cell Structures Found Only in Plant Cells Table
 Bacteria Cells
Bacteria Cells
- Bacteria, which have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, all share the following biological characteristics:
- They are?microscopic single-celled organisms
- Possess a?cell wall?(made of?peptidoglycan, not cellulose),?cell membrane,?cytoplasm?and?ribosomes
- Lack a nucleus?but contain a?circular chromosome of DNA that floats in the cytoplasm
- Plasmids?are sometimes present - these are?small rings of DNA?(also floating in the cytoplasm) that contain?extra genes?to those found in the chromosomal DNA
- They?lack mitochondria, chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles?found in animal and plant cells
- ?Some bacteria also have a?flagellum?(singular) or?several flagella?(plural). These are?long, thin, whip-like tails?attached to bacteria that allow them to?move
- Examples of bacteria include:
- Lactobacillus?(a rod-shaped bacterium used in the production of yoghurt from milk)
- Pneumococcus?(a spherical bacterium that acts as the pathogen causing pneumonia)
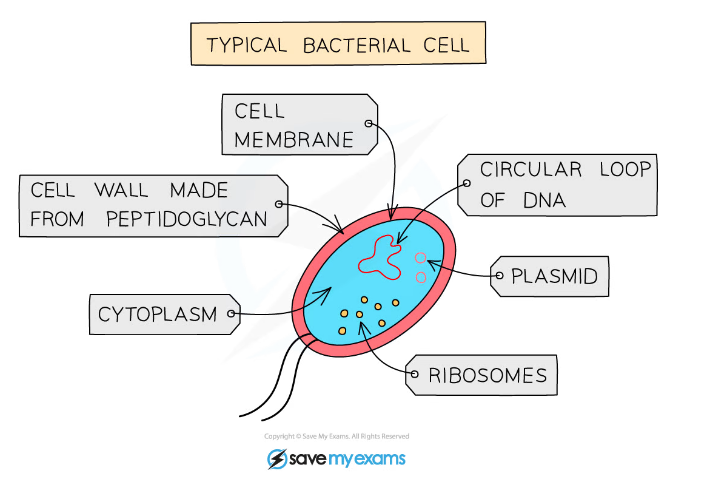 A typical bacterial cell
A typical bacterial cell
Identifying Cell Structures & Function
- Within the cytoplasm, the following organelles are visible in almost all cells except prokaryotes when looking at higher magnification (ie using an electron microscope):
- Mitochondria?(singular: mitochondrion) are organelles found throughout the cytoplasm
- Ribosomes?are tiny structures that can be free within the cytoplasm or attached to a system of membranes within the cell known as?Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes looks?rough?under the microscope; this gives rise to its name of?Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum?(often shortened to?R.E.R.)
- Vesicles?can also be seen using a higher magnification - these are small circular structures found moving throughout the cytoplasm
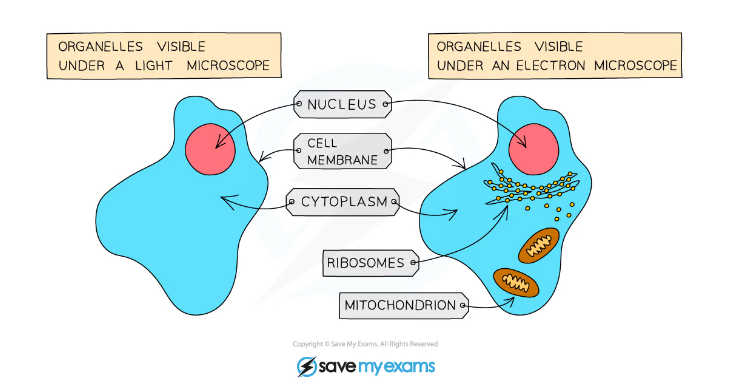 Structures in an animal cell visible under a light microscope and an electron microscope
Structures in an animal cell visible under a light microscope and an electron microscope
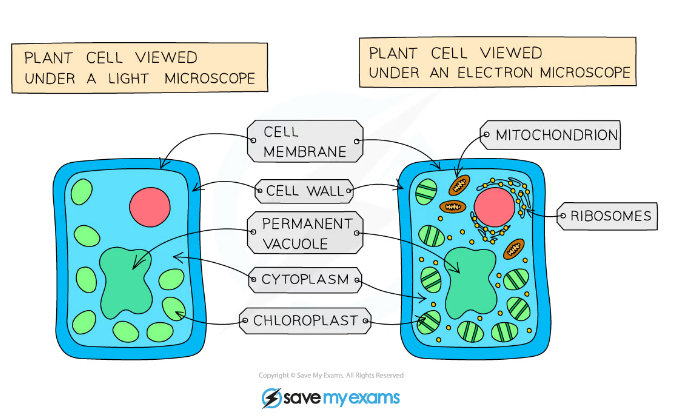 Structures in a plant cell visible under a light microscope and an electron microscope
Structures in a plant cell visible under a light microscope and an electron microscope










